Air fronts worksheet answer key – Welcome to the ultimate guide to air fronts! With our comprehensive answer key, you’ll master the ins and outs of these weather-shaping forces. From understanding their basics to predicting their impact, this guide has got you covered.
Air fronts play a crucial role in shaping our weather patterns. By delving into their characteristics, symbols, and movement, you’ll gain invaluable insights into weather forecasting and climate dynamics.
Air Fronts Basics
Air fronts are boundaries between two air masses with different temperatures and densities. They are significant in weather forecasting as they can bring about changes in temperature, humidity, and precipitation.
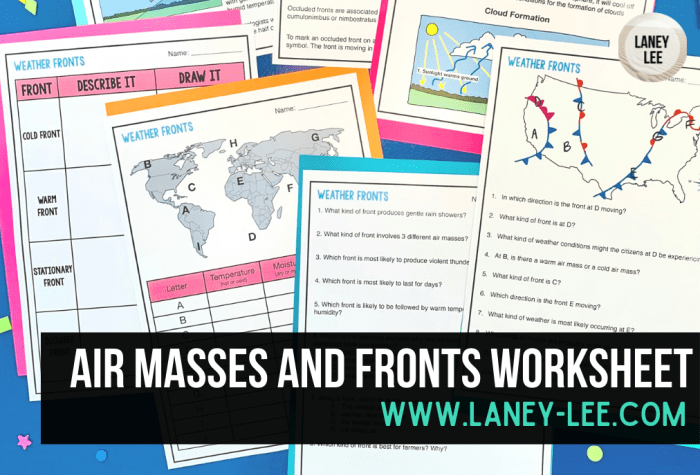
There are four main types of air fronts:
- Cold front:A cold air mass advances and replaces a warm air mass. Cold fronts are often associated with thunderstorms, heavy rain, and strong winds.
- Warm front:A warm air mass advances and replaces a cold air mass. Warm fronts are typically associated with drizzle, light rain, and fog.
- Stationary front:A cold air mass and a warm air mass meet and remain stationary. Stationary fronts can produce persistent cloud cover and drizzle.
- Occluded front:A cold front overtakes a warm front, lifting the warm air mass above the ground. Occluded fronts can produce heavy rain or snow.
Air fronts can significantly affect weather conditions. For example, a cold front can bring about a sudden drop in temperature, while a warm front can lead to an increase in humidity and precipitation.
Identifying Air Fronts on Weather Maps
Air fronts are boundaries between air masses with different temperatures and densities. They are important in weather forecasting because they can cause changes in temperature, humidity, and precipitation.
Air fronts are represented on weather maps by symbols that indicate the type of front and the direction in which it is moving. The most common types of air fronts are cold fronts, warm fronts, stationary fronts, and occluded fronts.
Locating and Identifying Air Fronts on Weather Maps, Air fronts worksheet answer key
To locate and identify air fronts on weather maps, look for lines that connect points of equal pressure. These lines are called isobars. Air fronts are typically located along or near isobars that are close together. The direction of the air front is indicated by the direction of the isobars.
For example, if the isobars are oriented north-south, the air front is oriented east-west. If the isobars are oriented east-west, the air front is oriented north-south.
Determining the Direction of Movement of Air Fronts
The direction of movement of an air front can be determined by looking at the pressure gradient across the front. The pressure gradient is the difference in pressure between two points. The greater the pressure gradient, the stronger the wind.
The wind will blow from the area of high pressure to the area of low pressure.
To determine the direction of movement of an air front, find the point where the pressure gradient is the greatest. The air front will be moving in the direction of the wind.
For example, if the pressure gradient is greatest to the east, the air front will be moving to the east.
Air Fronts and Climate Patterns: Air Fronts Worksheet Answer Key

Air fronts are pivotal in shaping regional climate patterns, influencing temperature, precipitation, and other climate variables. They act as boundaries between air masses with distinct properties, creating zones of contrasting weather conditions.
Temperature
Air fronts can significantly alter temperatures. When a cold front passes, it brings cooler air, leading to a drop in temperature. Conversely, warm fronts bring warmer air, causing temperatures to rise. These temperature changes can be abrupt, especially during the passage of strong fronts.
Precipitation
Air fronts play a crucial role in precipitation patterns. Cold fronts often bring precipitation, such as rain or snow, as the cold air mass pushes the warm air upward, causing it to condense and form clouds. Warm fronts, on the other hand, can produce precipitation as well, but it tends to be less intense and more widespread.
Long-term Climate Trends
Air fronts can also contribute to long-term climate trends. For instance, the position and frequency of air fronts can affect regional precipitation patterns, influencing vegetation growth and water availability. Over time, these changes can impact the overall climate of a region.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Air fronts are dynamic weather systems that can have significant impacts on weather conditions. Here are some case studies and real-world examples of how air fronts have affected historical weather events:
Great Blizzard of 1888
The Great Blizzard of 1888 was a powerful winter storm that paralyzed the northeastern United States. The storm was caused by a cold front that stalled over the region, bringing heavy snow and strong winds. The blizzard caused widespread power outages, transportation disruptions, and loss of life.
Air fronts worksheet answer key is available for download in PDF format. If you’re looking for information on the land sales full disclosure act , there are many resources available online. You can also find additional materials related to air fronts worksheet answer key by searching the web.
Hurricane Sandy
Hurricane Sandy was a powerful hurricane that made landfall in the United States in 2012. The storm was caused by a warm front that collided with a cold front, creating a massive storm system. Hurricane Sandy caused widespread flooding, power outages, and damage to infrastructure.
Challenges and Limitations of Using Air Fronts for Weather Forecasting
While air fronts are important for weather forecasting, there are some challenges and limitations to their use. One challenge is that air fronts can be difficult to track, especially in areas with complex terrain. Additionally, air fronts can sometimes change direction or speed unexpectedly, which can make it difficult to predict their impact on weather conditions.
Advanced Concepts in Air Front Analysis
Beyond basic identification, advanced techniques enhance air front analysis for precise weather forecasting. These involve leveraging numerical weather prediction models and visualization methods.
Numerical Weather Prediction Models
Numerical weather prediction (NWP) models simulate atmospheric conditions using mathematical equations. By incorporating real-time data and historical patterns, these models forecast weather conditions, including air front movements.
NWP models provide:
- High-resolution data on air front positions and intensities
- Predictions of air front movements and interactions
- Ensemble forecasting to assess uncertainty and improve accuracy
Visualization and Interpretation
Visualizing air front data helps meteorologists identify patterns and trends. Techniques include:
- Isobars:Lines connecting points of equal atmospheric pressure, indicating pressure gradients and air front locations
- Frontogenesis functions:Mathematical equations that predict the formation and strengthening of air fronts
- Satellite imagery:Infrared and visible light images that reveal cloud patterns associated with air fronts
By interpreting these visualizations, meteorologists can:
- Identify air front types and their orientations
- Forecast the timing and location of air front passages
- Assess the potential for severe weather associated with air fronts
Improved Forecasting Accuracy
Advanced air front analysis techniques significantly improve weather forecasting accuracy by:
- Providing precise location and intensity forecasts of air fronts
- Predicting the timing and duration of air front passages
- Identifying areas at risk for severe weather, such as thunderstorms and tornadoes
Essential Questionnaire
What are air fronts?
Air fronts are boundaries between air masses with different temperatures and densities.
How can I identify air fronts on a weather map?
Look for symbols like blue lines with triangles (cold fronts) and red lines with semicircles (warm fronts).
How do air fronts affect weather?
They can bring changes in temperature, humidity, cloud cover, and precipitation.