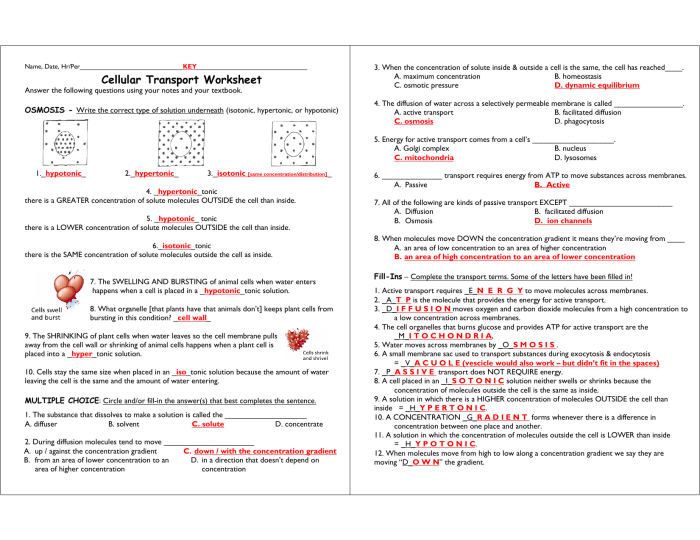
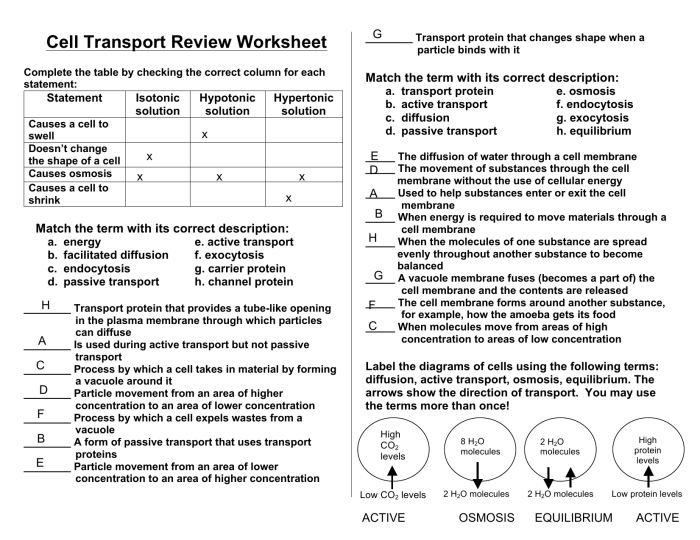
Welcome to our comprehensive guide to cell transport review worksheet answers pdf. This in-depth resource is designed to provide a thorough understanding of the fundamental concepts, mechanisms, and applications of cell transport. As we delve into this fascinating topic, you’ll gain a deeper appreciation for the critical role cell transport plays in sustaining life and driving biological processes.
Throughout this guide, we’ll explore the different types of cell transport, including passive and active transport, and delve into the mechanisms that govern each type. We’ll also examine the factors that influence the rate and efficiency of cell transport and highlight its vital importance in various biological functions, such as nutrient uptake, waste removal, and cell signaling.
Cell Transport: Definition and Overview
Cell transport is the movement of molecules across the cell membrane. It is essential for various biological processes, such as nutrient uptake, waste removal, and cell signaling. The understanding of cell transport has evolved significantly over time, with major advancements in the 19th and 20th centuries.
Types of Cell Transport
Passive Transport, Cell transport review worksheet answers pdf
Passive transport involves the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, without the need for energy input. It includes diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion.
Active Transport
Active transport requires energy input to move molecules against a concentration gradient, from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. It includes primary active transport and secondary active transport.
Factors Affecting Cell Transport
Several factors can affect the rate and efficiency of cell transport, including:
- Temperature
- Concentration gradients
- Membrane permeability
- Surface area of the membrane
Importance of Cell Transport: Cell Transport Review Worksheet Answers Pdf
Cell transport plays a crucial role in various biological functions, including:
- Nutrient uptake
- Waste removal
- Cell signaling
- Maintaining cell volume
Examples of Cell Transport
Cell transport occurs in various biological systems, including:
- Plant water uptake
- Animal respiration
- Nerve impulse transmission
- Drug delivery
Applications of Cell Transport
An understanding of cell transport has led to advancements in various fields, such as:
- Medicine (drug delivery, gene therapy)
- Biotechnology (tissue engineering, bioremediation)
Questions Often Asked
What is the significance of cell transport in biological systems?
Cell transport is crucial for maintaining homeostasis, facilitating nutrient uptake, removing waste products, and enabling cell signaling. It underpins essential processes such as respiration, photosynthesis, and nerve impulse transmission.
How does the rate of cell transport vary depending on factors like temperature and concentration gradients?
The rate of cell transport is directly proportional to temperature and concentration gradients. Higher temperatures increase the kinetic energy of molecules, facilitating faster transport. Concentration gradients drive the movement of molecules from areas of high concentration to low concentration.
What are some practical applications of cell transport in medicine and biotechnology?
Cell transport principles are applied in drug delivery systems, gene therapy, and tissue engineering. Understanding cell transport mechanisms enables researchers to develop targeted drug delivery methods, improve gene therapy efficiency, and engineer tissues for regenerative medicine.