Label the structures of the thoracic cavity. – Label the structures of the thoracic cavity sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. The thoracic cavity, a region of paramount importance within the human body, houses vital organs responsible for respiration, circulation, and digestion.
This article delves into the intricacies of this anatomical marvel, meticulously labeling and describing its major structures to provide a comprehensive understanding of their location, function, and interconnectedness.
Thoracic Cavity Overview
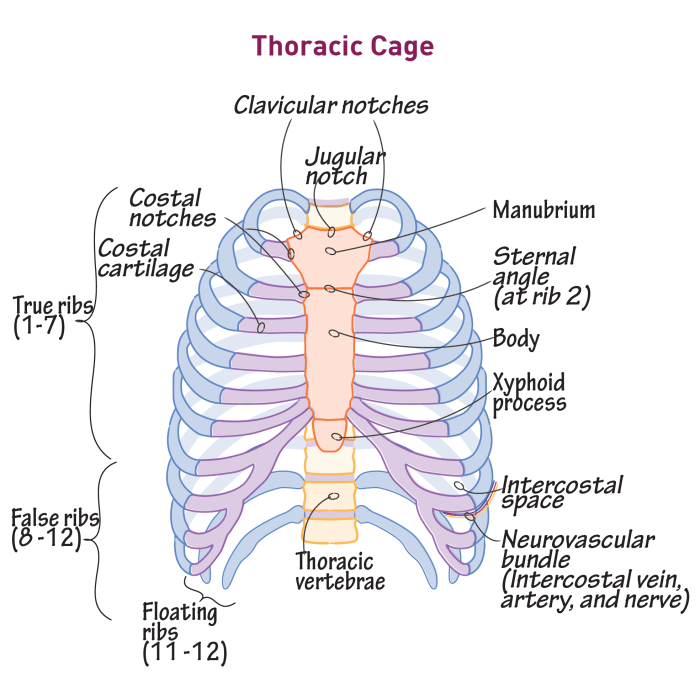
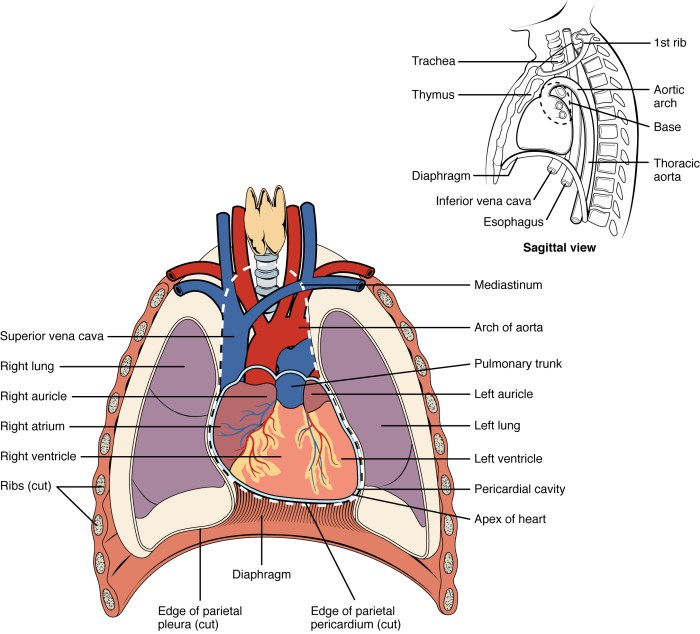
The thoracic cavity, also known as the chest cavity, is a region of the body located between the neck and the abdomen. It is bounded by the ribs and sternum anteriorly, the thoracic vertebrae posteriorly, and the diaphragm inferiorly.
The thoracic cavity houses vital organs such as the heart, lungs, esophagus, and major blood vessels and nerves. It plays a crucial role in respiration, circulation, and digestion.
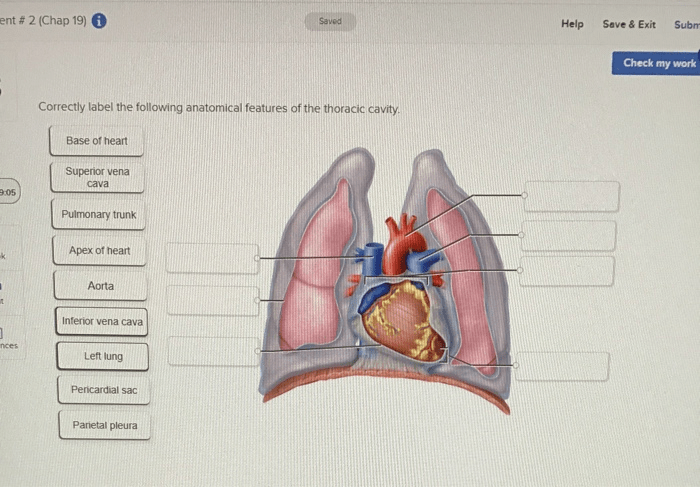
Structures of the Thoracic Cavity, Label the structures of the thoracic cavity.
The thoracic cavity contains numerous structures, including:
- Heart
- Lungs
- Esophagus
- Trachea
- Aorta
- Vena cava
- Diaphragm
Organs of the Thoracic Cavity
The heart, lungs, and esophagus are the primary organs located within the thoracic cavity.
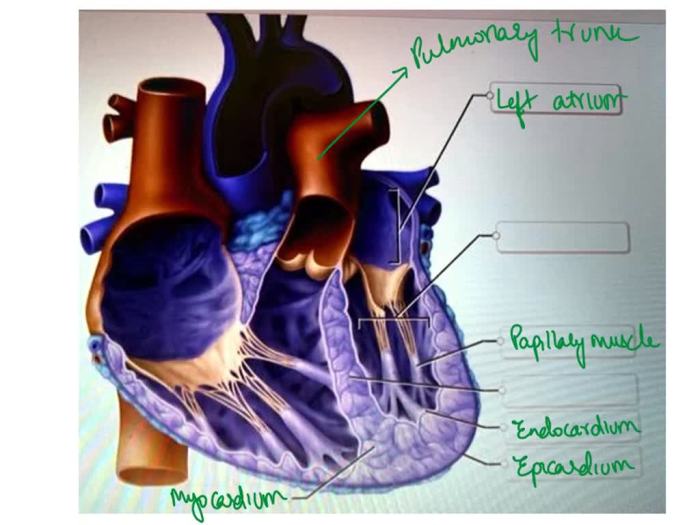
Heart
The heart is a muscular organ responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. It is located medially in the thoracic cavity and is divided into four chambers: the right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle.
Lungs
The lungs are a pair of spongy organs responsible for gas exchange. They are located on either side of the heart and are divided into lobes: the right lung has three lobes, while the left lung has two.
Esophagus
The esophagus is a muscular tube that transports food from the mouth to the stomach. It passes through the thoracic cavity and is located posterior to the heart and lungs.
Blood Vessels and Nerves of the Thoracic Cavity
The thoracic cavity contains several major blood vessels and nerves:
Blood Vessels
- Aorta: The main artery that carries oxygenated blood away from the heart.
- Vena cava: The main veins that return deoxygenated blood to the heart.
- Pulmonary artery: The artery that carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs.
- Pulmonary vein: The vein that carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart.
Nerves
- Vagus nerve: The longest nerve in the body, which innervates the heart, lungs, and other organs in the thoracic and abdominal cavities.
- Phrenic nerve: The nerve that innervates the diaphragm.
Muscles of the Thoracic Cavity
The muscles involved in respiration are located in the thoracic cavity:
Intercostal Muscles
The intercostal muscles are located between the ribs. They contract and relax to expand and contract the chest cavity during respiration.
Diaphragm
The diaphragm is a large, dome-shaped muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity. It contracts and relaxes to expand and contract the chest cavity during respiration.
Common Queries: Label The Structures Of The Thoracic Cavity.
What are the major organs located within the thoracic cavity?
The thoracic cavity houses the heart, lungs, esophagus, and thymus.
What is the function of the thoracic cavity?
The thoracic cavity provides protection for the vital organs it contains and facilitates respiration by housing the lungs.
How are the structures of the thoracic cavity interconnected?
The structures of the thoracic cavity are interconnected through a network of blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissues, ensuring their coordinated functioning.